AI Agents for Agritech
An advanced Multi-Agent Assistant leveraging AI agents, APIs, and RAG for precise agricultural insights.
Modern agriculture demands intelligent systems capable of synthesizing vast amounts of data into actionable advice. Agrigraph is a sophisticated assistant, created for a European project, that orchestrates multiple AI agents to provide farmers and agronomists with real-time weather data, historical analysis, and precise irrigation recommendations based on project documentation and sensor simulations.
Objectives
- Orchestrate specialized AI agents for multi-domain agricultural support.
- Integrate real-time and historical weather services (Open-Meteo).
- Implement Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for querying technical agricultural documents.
- Provide data-driven irrigation recommendations using tensiometer predictions.
My Role
- Architected the multi-agent system using LangGraph and LangChain.
- Developed custom tools for weather data retrieval and coordinate conversion.
- Integrated a FAISS-based RAG pipeline for document intelligence.
- Implemented the irrigation logic and agent orchestration workflows.
Tech Stack
| Language | Python 3.11+ |
|---|---|
| Frameworks | LangGraph, LangChain |
| Models | Google Gemini (Generative AI) |
| Vector DB | FAISS (Facebook AI Similarity Search) |
| DevOps | uv, YAML files |
Repository Structure
The project follows a modular graph-based architecture:
agentsSpecialist agent definitions and utilitiestoolsCustom implementations for Weather, RAG, and SensorsgraphLangGraph workflow and state orchestrationconfigYAML-based agent prompts and model settings
The Challenge: Fragmented Agricultural Intelligence
Decision-making in the field is often hindered by the difficulty of accessing and combining diverse information sources. Technical manuals, real-time weather forecasts, and soil sensor data are frequently disconnected, leading to suboptimal crop management.
Agrigraph solves this by acting as a Unified Knowledge Hub. The system integrates:
- Weather Intelligence: Automated retrieval of coordinates and meteorological data.
- Document Wisdom: RAG-powered querying of the IRRITRE project documentation.
- Sensor Insights: Predictive tools for soil moisture and irrigation needs.
- General Agronomy: A fallback agent for broad agricultural queries.
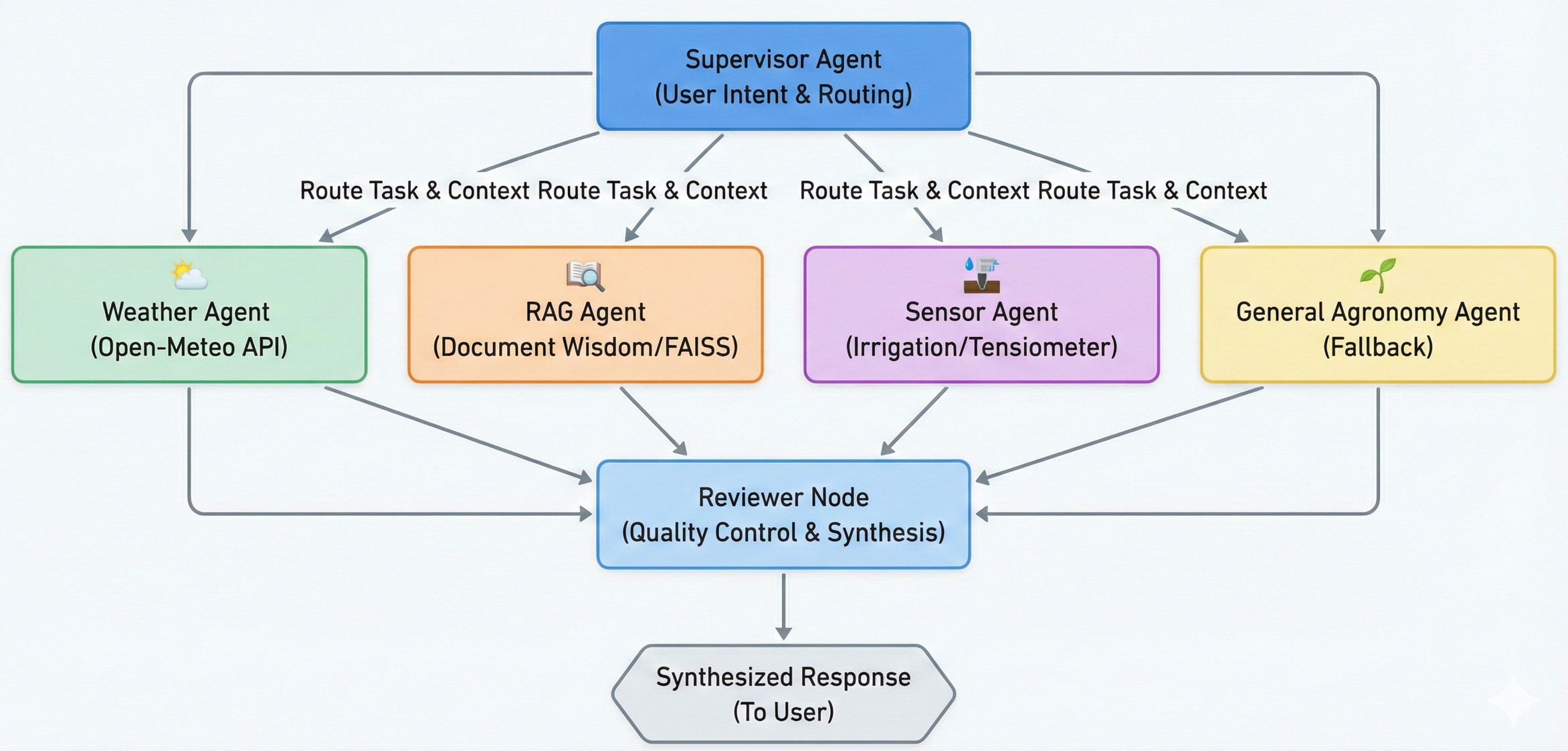
Methodology & Orchestration
Agrigraph utilizes a state-of-the-art multi-agent architecture to handle complex requests:
- Supervisor Agent: Analyzes user intent and routes tasks to the most qualified specialists, allowing for parallel task execution and response synthesis.
- Specialized Tooling: Each agent has access to specific tools (Open-Meteo API, FAISS vector stores, tensiometer models) to ensure high-fidelity responses.
- Reviewer Node: A final quality-control layer that refines the aggregated response for clarity and tone consistency.
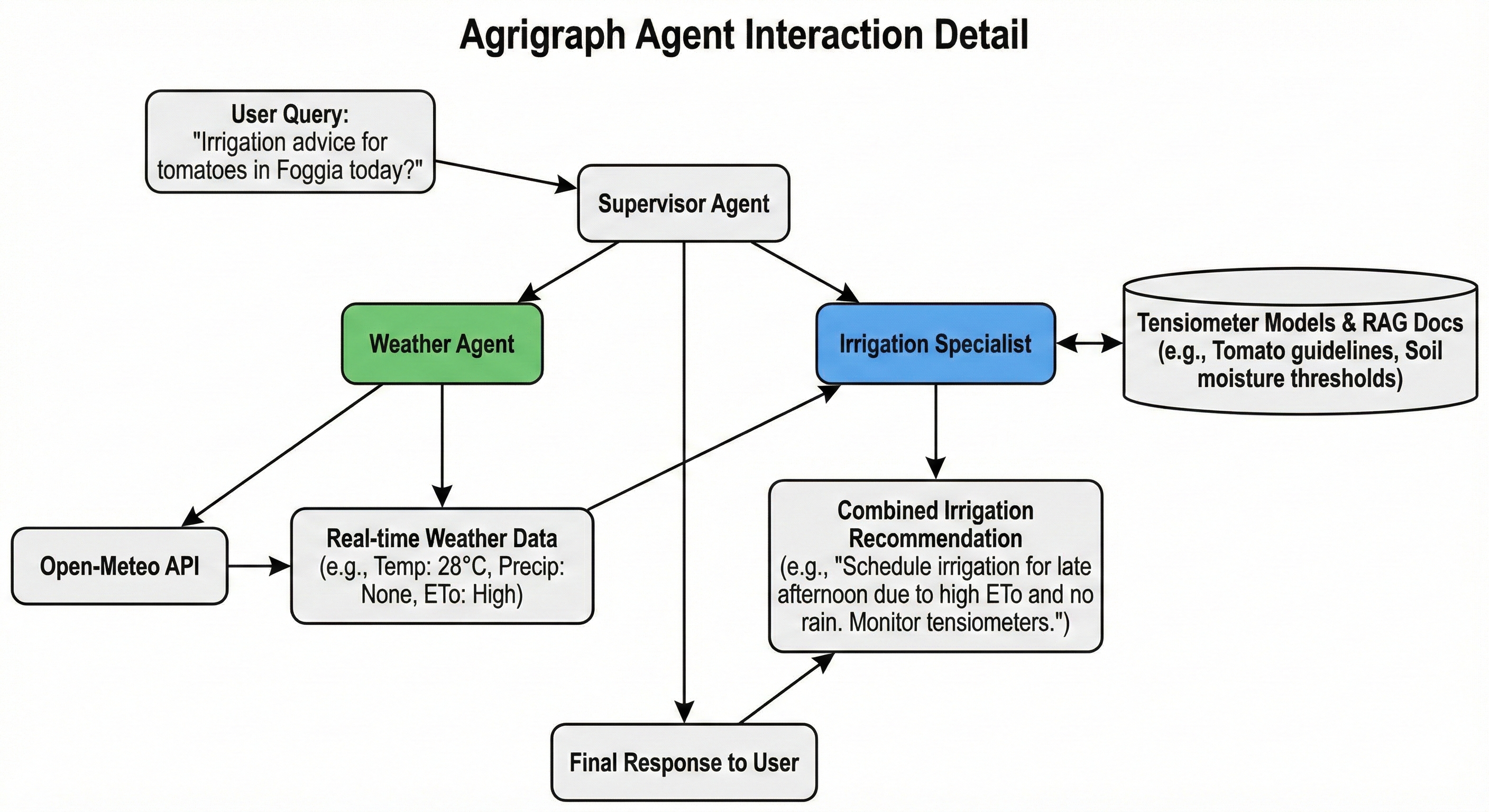
Results: Precision at Scale
By leveraging LLMs for both reasoning and data retrieval, Agrigraph provides a robust platform for digital agriculture.
Key outcomes:
- Context-Aware Support: Answers complex questions by combining technical docs with real-time conditions.
- Simplified Access: Users interact with a natural language interface instead of raw data silos.
- Extensibility: The graph-based design allows for easy integration of new tools and sensors as the project evolves.
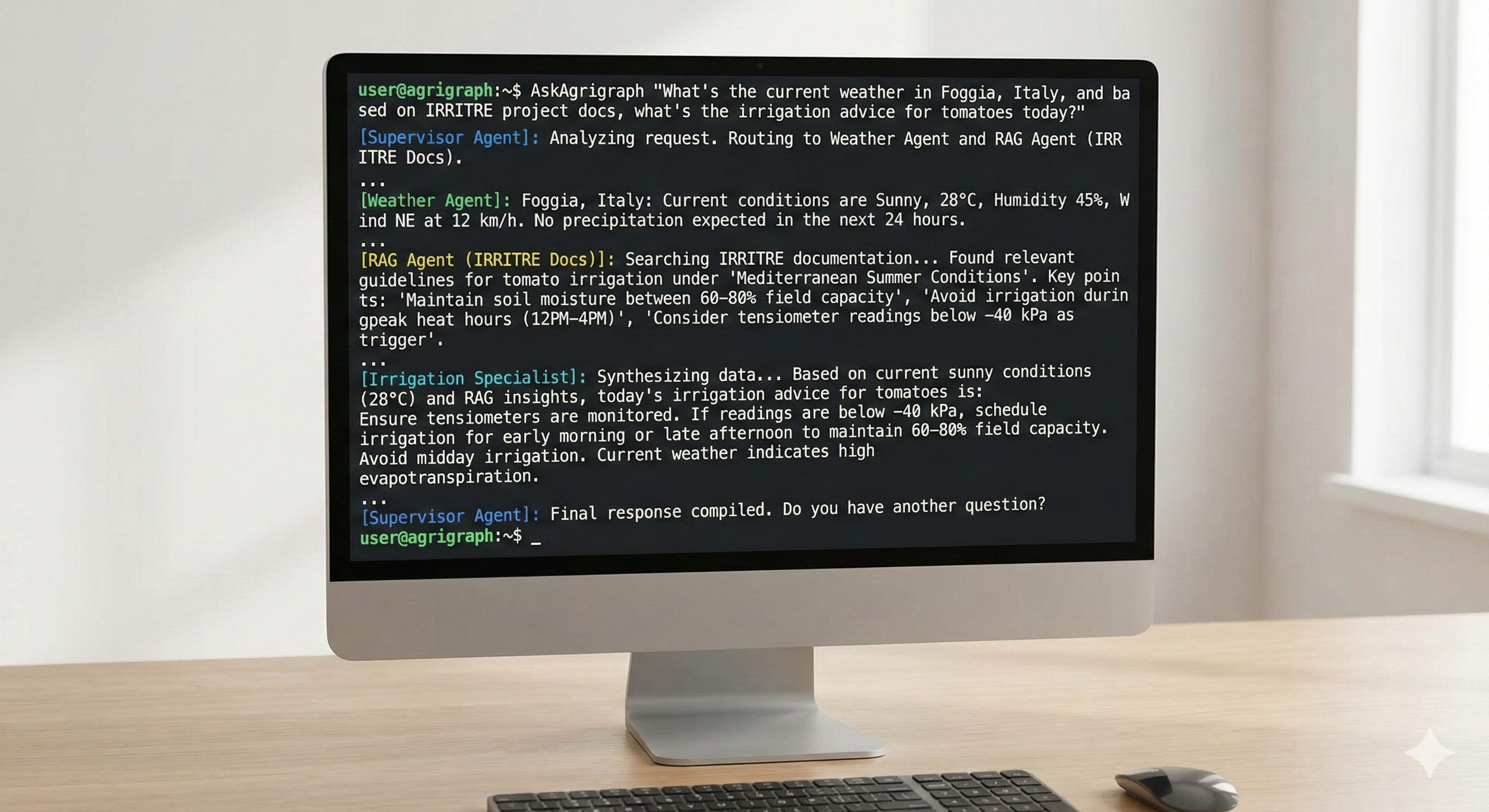
Note: This image is a placeholder and does not display real production data.
Note: To maintain confidentiality, all company names, locations, dates, and specific proprietary values have been anonymized or modified. The analysis focuses on the technical methodology and challenges encountered during the project.