Full MLOps Workflow
Advanced data integration and predictive modeling for precision irrigation using physical and machine learning approaches.
Efficient water management in agriculture requires more than just raw data; it demands the integration of diverse information sources into actionable predictive models. SoilCast is a comprehensive framework for the European AI Factory project that synchronizes field sensors, weather forecasts, and crop physiology to optimize irrigation scheduling.
Objectives
- Integrate heterogeneous data sources, including IoT sensors, weather stations, remote sensing, and soil properties.
- Deploy and benchmark predictive models for soil moisture and water requirements.
- Provide a modular, automated pipeline for data preprocessing and model execution.
My Role
- Collaborated closely with colleagues to design the overall framework architecture.
- Implemented automated cleaning, resampling, and transformation logic.
- Integrated the AquaCrop-OSPy physical model into the workflow.
- Orchestrated the entire pipeline using Prefect for robust, automated execution.
Tech Stack
| Language | Python 3.11+ |
|---|---|
| Orchestration | MLflow, Prefect |
| Models | AquaCrop-OSPy, XGBoost |
| Analysis | NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn |
| DevOps | uv, YAML files |
Repository Structure
The project follows a modular pipeline design:
configYAML parameters for models and APIspipelinesModular pipelines for all the stages of the workflow, from data preprocessing to model executiondataMulti-stage storage (Input/Output) for the workflowtoolsUtility scripts for data handling
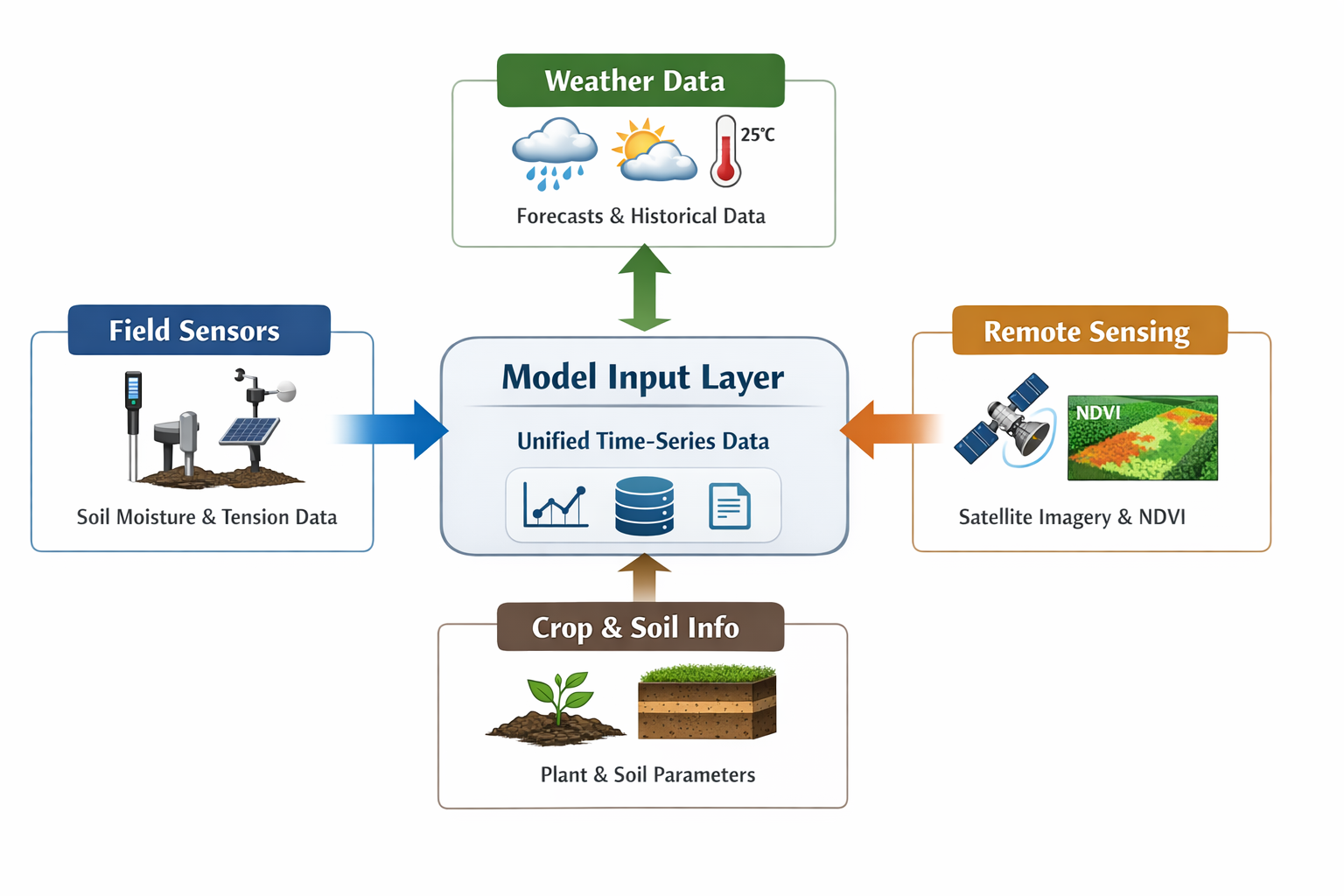
The Challenge: Heterogeneous Data Integration
Precision irrigation often fails because agricultural data is fragmented across different formats and temporal resolutions. Weather forecasts, local sensor measurements, and satellite imagery are often siloed, making predictive modeling difficult.
SoilCast addresses this challenge by building a unified Model Input layer. The pipeline ingests:
- Field Sensors: Real-time soil moisture and tension data.
- Weather Data: Historical records and multi-day forecasts.
- Crop & Soil Info: Static parameters defining plant physiology and soil hydraulic properties.
- Remote Sensing: Vegetation indices to calibrate crop growth.
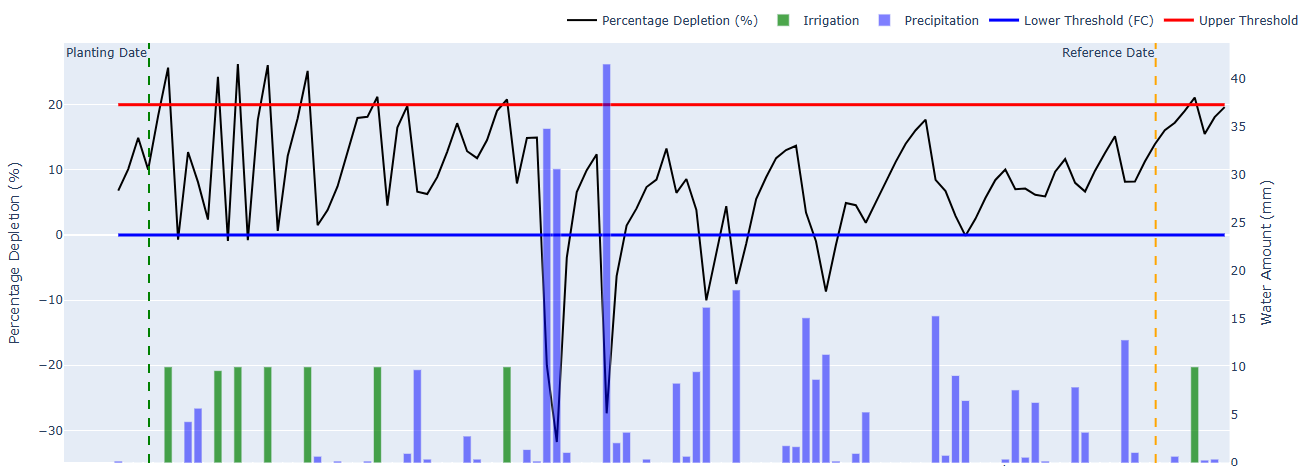
Methodology & Modeling
SoilCast implements a dual approach for irrigation prediction:
- Physical Modeling (AquaCrop): Using the FAO AquaCrop-OSPy engine to simulate the soil-water-plant-atmosphere balance, providing a mechanistic understanding of water stress and crop yield impact.
- Machine Learning (XGCast): A gradient-boosted model (XGBoost) trained on historical sensor and weather data to forecast short-term soil moisture trends.
Results: Predictive Insights
By combining physical constraints with machine learning flexibility, SoilCast provides a robust decision-support system.
Key outcomes:
- Early Warning: Predict potential water stress events up to 7 days in advance.
- Scenario Analysis: Compare different irrigation strategies (e.g., deficit irrigation vs. full requirements).
- Scalability: Prefect-based architecture enables scaling across multiple consortia and hundreds of fields.
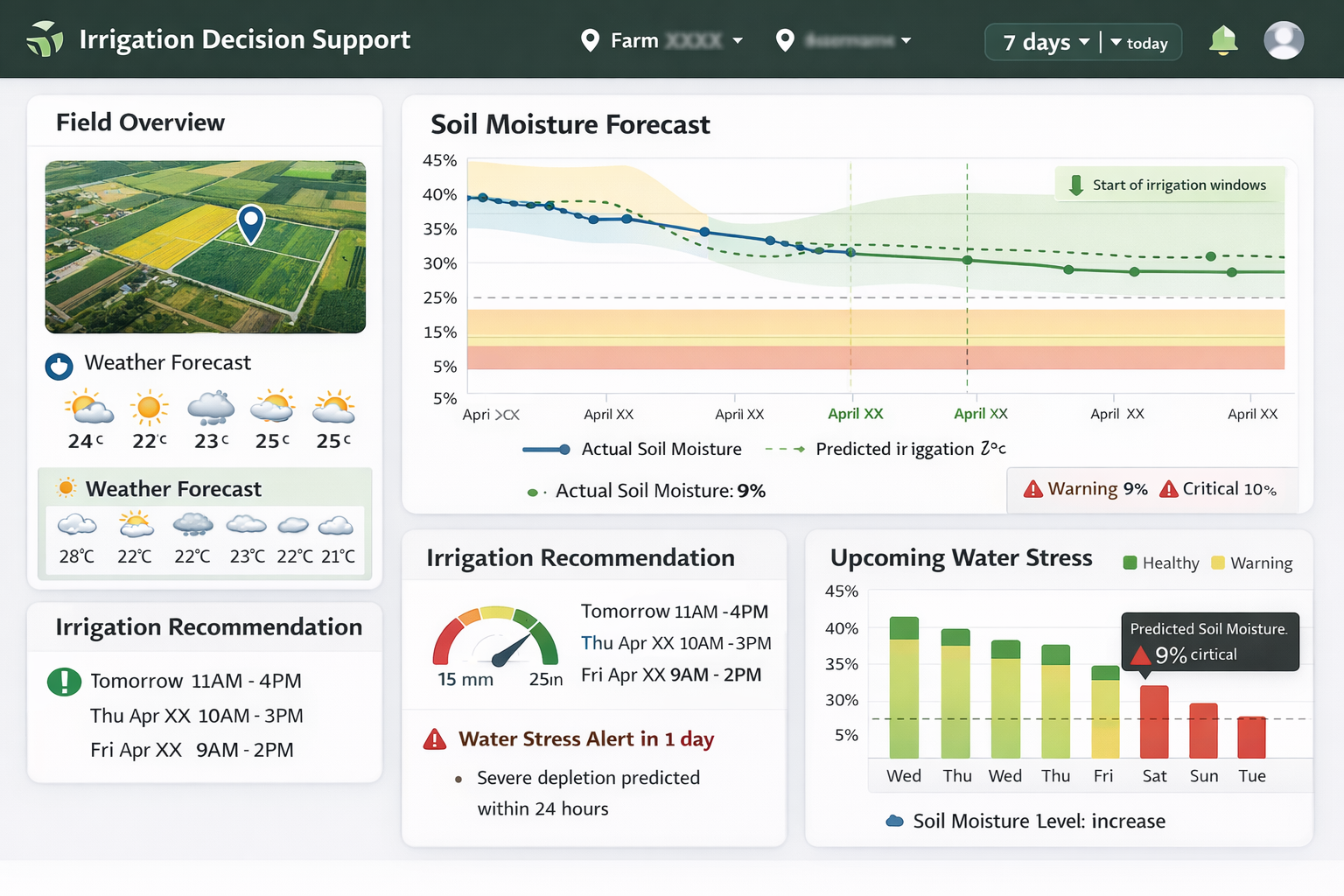
Note: This dashboard is a mockup and does not display real data.
Note: To maintain confidentiality, all company names, locations, dates, and specific proprietary values have been anonymized or modified. The analysis focuses on the technical methodology and challenges encountered during the project.